ALLIGATORS AND CROCODILES
 Let's start with alligators and crocodiles. Of the reptiles on Earth, the alligators, crocodiles, and others of this type are the largest around. Did you know that some of them get larger than 18 feet long (over 6 meters)? This group of reptiles is called Crocodilia even though they aren't all crocodiles. Some scientists think that they are more closely related to birds than any other reptile. If you're out looking for one, you'll find them near the water in warmer climates. Reptiles don't do well in the cold.
Let's start with alligators and crocodiles. Of the reptiles on Earth, the alligators, crocodiles, and others of this type are the largest around. Did you know that some of them get larger than 18 feet long (over 6 meters)? This group of reptiles is called Crocodilia even though they aren't all crocodiles. Some scientists think that they are more closely related to birds than any other reptile. If you're out looking for one, you'll find them near the water in warmer climates. Reptiles don't do well in the cold.
SNAKES AND LIZARDS
Both snakes and lizards are in the order calledSquamata. Snakes are special because they have no legs. You knew that fact. But did you know that snakes don't have ears? They feel vibrations and smell with their tongues. Did you know that snakes can unhook their jaws so that they can swallow prey that is actually wider than they are? Very cool. Don't worry about snakes being slimy. They aren't. They are just very shiny because of their specialized scales.With so many types of lizards, we don't know where to begin. Lizards have scales just like snakes. They also have legs. They can dig, climb trees, and grab things. It's very handy to be able to grab on to things. Those legs and feet are also placed under the body, so they can walk around without hitting the ground.












 We asked it before. What would give you an advantage if you were a plant? You have a vascular system to transport nutrients. You have seeds for reproduction that allow your babies to spread out in new areas. What next? Flowers! Flowers are the most recent evolutionary advantage for plants.
We asked it before. What would give you an advantage if you were a plant? You have a vascular system to transport nutrients. You have seeds for reproduction that allow your babies to spread out in new areas. What next? Flowers! Flowers are the most recent evolutionary advantage for plants. Those specialized flowers are able to attract organisms to help pollinate and distribute seeds. Another cool advantage is the fruit/seed packaging. Would you rather eat a pine cone or an apple? A lot of animals would go for the apple. When they do, they are able to spread the seeds across wide areas after the animal poops out the seeds.
Those specialized flowers are able to attract organisms to help pollinate and distribute seeds. Another cool advantage is the fruit/seed packaging. Would you rather eat a pine cone or an apple? A lot of animals would go for the apple. When they do, they are able to spread the seeds across wide areas after the animal poops out the seeds. The other kind of plant in the flowering plant world is called a dicot. Dicot is short for dicotyledon. "Di" means two or a double cotyledon. These plants have seeds that have two cotyledons, two seed leaves of food for the embryo. Most of the flowers you see every day are dicots. They have flowers with petals in numbers of four and five. They also have really complex leaves with veins all over, not long like monocots. Some examples of dicots are roses, sunflowers, cacti, apple, and cherry plants.
The other kind of plant in the flowering plant world is called a dicot. Dicot is short for dicotyledon. "Di" means two or a double cotyledon. These plants have seeds that have two cotyledons, two seed leaves of food for the embryo. Most of the flowers you see every day are dicots. They have flowers with petals in numbers of four and five. They also have really complex leaves with veins all over, not long like monocots. Some examples of dicots are roses, sunflowers, cacti, apple, and cherry plants.  So you've got a vascular system. What comes next? Seeds. Seeds let you send your offspring out into the world. Seeds provide a protective coat so that the embryo plant can develop when it finds a nice piece of soil. But remember this: gymnosperms have not developed the ability to make flowers. Flowers are an evolutionary advancement after seeds. So if you have a vascular system, seeds, and no flowers, what are you? A gymnosperm!
So you've got a vascular system. What comes next? Seeds. Seeds let you send your offspring out into the world. Seeds provide a protective coat so that the embryo plant can develop when it finds a nice piece of soil. But remember this: gymnosperms have not developed the ability to make flowers. Flowers are an evolutionary advancement after seeds. So if you have a vascular system, seeds, and no flowers, what are you? A gymnosperm!
 Not every plant made it to the modern day. Fossil evidence shows what plants used to be alive in other geological eras. The Ginkgo is one of the ones that made it. Some people call it a "Maidenhair Tree". It's the last one of its kind. It has needles that have combined to form very sturdy leaf-like structures. You need to remember they are not like leaves in the traditional sense. You've probably seen these all over. Landscape designers love to use them because they look very nice and are very resistant to pollution. They are great for cities. Being able to resist insects and disease has let this species survive beyond all of its close relatives.
Not every plant made it to the modern day. Fossil evidence shows what plants used to be alive in other geological eras. The Ginkgo is one of the ones that made it. Some people call it a "Maidenhair Tree". It's the last one of its kind. It has needles that have combined to form very sturdy leaf-like structures. You need to remember they are not like leaves in the traditional sense. You've probably seen these all over. Landscape designers love to use them because they look very nice and are very resistant to pollution. They are great for cities. Being able to resist insects and disease has let this species survive beyond all of its close relatives.  We're going to look at plant structure in this section. The plants we discuss will be vascular plants that have systems of tubes (xylem and phloem) for the transport of nutrients and water. Remember that there is a wide variety of plants on Earth and even a whole group that doesn't havevascular systems. Mosses and liverworts may still have photosynthesis, but they do not have that 'classic' plant structure. Then you will find species such as cacti that don't have leaves. They conductphotosynthesis in their stems. Anyway, just remember that there are many other possibilities in the plant kingdom.
We're going to look at plant structure in this section. The plants we discuss will be vascular plants that have systems of tubes (xylem and phloem) for the transport of nutrients and water. Remember that there is a wide variety of plants on Earth and even a whole group that doesn't havevascular systems. Mosses and liverworts may still have photosynthesis, but they do not have that 'classic' plant structure. Then you will find species such as cacti that don't have leaves. They conductphotosynthesis in their stems. Anyway, just remember that there are many other possibilities in the plant kingdom.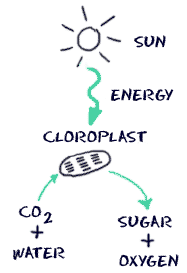 Not all of the light from the Sun makes it to the surface of the Earth. Even the light that does make it here is reflected and spread out. The little light that does make it here is enough for the plants of the world to survive and go through the process of photosynthesis. Light is actually energy, electromagnetic energy to be exact. When that energy gets to a green plant, all sorts of reactions can take place to store energy in the form of sugar molecules.
Not all of the light from the Sun makes it to the surface of the Earth. Even the light that does make it here is reflected and spread out. The little light that does make it here is enough for the plants of the world to survive and go through the process of photosynthesis. Light is actually energy, electromagnetic energy to be exact. When that energy gets to a green plant, all sorts of reactions can take place to store energy in the form of sugar molecules. The whole process doesn't happen all at one time. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two main parts. The first part is called the light dependent reaction. This reaction happens when the light energy is captured and pushed into a chemical called ATP. The second part of the process happens when the ATP is used to make glucose (the Calvin Cycle). That second part is called the light independent reaction.
The whole process doesn't happen all at one time. The process of photosynthesis is divided into two main parts. The first part is called the light dependent reaction. This reaction happens when the light energy is captured and pushed into a chemical called ATP. The second part of the process happens when the ATP is used to make glucose (the Calvin Cycle). That second part is called the light independent reaction.